
Lemborexant (brand name DAYVIGO™) has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of insomnia in adults.


Lemborexant (brand name DAYVIGO™) has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of insomnia in adults.

Each moment of each day we make choices that can affect our brain health-our challenge is, without judgment, to increase the choices that promote a healthy brain.

The fallout from burnout: alcohol dependence, binge eating, sleep disorders, and general ill health.

Even as antidepressants improve mood, they can worsen sleep-and poor sleep is both a symptom and a cause of depression.

Blue spectrum light can worsen two systems that are already fragile in people with mood disorders: sleep and circadian rhythms. Fortunately, there are simple solutions to correct this problem.

Which tool is useful to measure night-to-night variability, sleep onset latency, and sleep duration in those with ADHD?

Two evidence-based psychosocial treatments are available for trauma-based nightmares. The authors provide a case illustration for each method.

Improving sleep hygiene is very effective and low-risk in older adults. Which habits work best and which should be avoided? Take the quiz and learn more.

Given the impact of sleep on quality of life, cognitive functioning, and health outcomes, understanding sleep disorders in older adults is vital to their overall care.

Which sleep parameters are increased in alcohol use disorders? Take the quiz and learn more.

This article reviews current literature on insomnia and alcohol use disorders and highlights assessment and treatment of sleep disorders in patients with comorbid alcohol abuse.

The Chair of a Special Report on substance abuse disorders describes the highlights of 6 articles in the series.

Here: suggested strategies for assessment and management of this circadian sleep disorder commonly seen in adolescents.

A single approach combines potent elements from 5 bipolar-specific therapies.

Here’s the major ingredient in a new psychotherapy for bipolar disorder.

A humorous cure for insomnia.

Concerned about daylight savings time? This patient handout offers tips for getting a good night's sleep.

A quiz on complex sleep-related behaviors.

A study has found that induction of slow waves during early non-rapid eye movement sleep may improve executive function in children with ADHD.

DSM-5 sleep-wake disorders are now more in sync with other medical disorders and sleep disorders classificatory systems. Here's what's changed.

Here's a brief history of sleepwalking, associated factors, and pathology; sleep-related violence and forensic considerations; and management strategies.

Here's an update on parasomnias-the undesirable physical, experiential, or behavioral phenomena that occur exclusively during sleep onset, during sleep, or during arousals from sleep.

All psychiatrists know the risk factors for suicide. Among the newest modifiable risk factors to join the list are insomnia and nightmares.

Sleep disorders represent a significant problem in patients with Alzheimer disease. Here: assessment strategies and a review of drug and non-drug interventions.
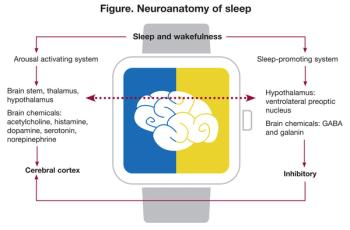
Sleep-related problems are among the most disabling consequences of TBI, with multiple influences: impairment of neuronal plasticity, metabolomic alterations, loss of vascular homeostasis, and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. The authors take a close look.