
Stories covered in the January issue included gun violence, physician burnout and depression, mental health/HIV, young adult psychiatry, women's issues, and other topics of interest to clinicians.

Stories covered in the January issue included gun violence, physician burnout and depression, mental health/HIV, young adult psychiatry, women's issues, and other topics of interest to clinicians.

Many college students who engage in binge drinking, experiment with illicit drugs, and/or misuse pharmaceuticals will go through this rite of passage relatively unscathed. However, others will not.

In the years of transition to adulthood, obtaining adequate assessment and treatment for ADHD is often more difficult than at any other point during the lifespan.

The research on electronic aggression among college students indicates that it is highly prevalent, with over 93% of college students reporting some negative effects due to electronic victimization.
Strategies to decrease the chances that individuals will fall through the cracks in the college years.

The challenges in providing mental health care to the college community are significant. Here's a brief look at the issues.

For all its popular appeal, the science that has emerged on cannabis use does not look good--especially for the teenage brain.

Psychiatrists can provide significant support and insight to patients who are now coming to campus with a wide array of mental health challenges.

Who is responsible for treating the adolescent and young adult with psychiatric issues -- and when and how should transitions in care occur?

Jails have a much higher percentage of homeless mentally ill than does the general community, and those with psychiatric disorders (eg, schizophrenia) must often fend for themselves. Here are some solutions.

Currently, 1 in 15 youths undergoing psychiatric evaluation in the emergency department is restrained. This article covers diagnostic and therapeutic interventions that can reduce fear and put the young patient on a path to recovery.
It is important to recognize and document the abilities and deficits of a patient in order to determine capacity.

Acute intoxication is the most likely culprit for an increased risk of violence or agitation, but personality, psychosis, and cognitive problems can all play a role. A skilled clinician can glean a great deal of information in a short period of time.

With a consistent and evolving presence in the US, forensic psychiatry has grown increasingly complex, with many specialty areas under its subspecialty umbrella.

Psychiatrists should not be afraid to assess parenting issues and other stressors when treating depressed or psychotic parents of young children.

About 25% of children in the US live with only one parent; the fallout from contentious divorces often leaves them susceptible to any number of damaging scenarios.

This article reviews a wide array of medicolegal, risk management, regulatory, and forensic mental health issues in the older population, which is growing at an accelerated rate.
Reporting of symptoms that are beyond available medical evidence is a central feature of malingering and related conditions, making the clinical differentiation of these disorders a challenge.

This article focuses primarily on the issues facing a psychiatrist who has been retained as an expert witness in a will or trust contest involving claims of a lack of capacity.

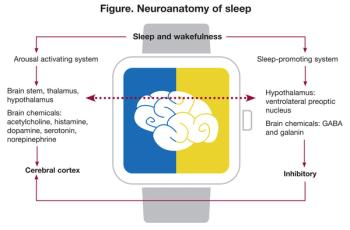
DSM-5 sleep-wake disorders are now more in sync with other medical disorders and sleep disorders classificatory systems. Here's what's changed.

Here's a brief history of sleepwalking, associated factors, and pathology; sleep-related violence and forensic considerations; and management strategies.

Here's an update on parasomnias-the undesirable physical, experiential, or behavioral phenomena that occur exclusively during sleep onset, during sleep, or during arousals from sleep.

All psychiatrists know the risk factors for suicide. Among the newest modifiable risk factors to join the list are insomnia and nightmares.

Sleep disorders represent a significant problem in patients with Alzheimer disease. Here: assessment strategies and a review of drug and non-drug interventions.
Sleep-related problems are among the most disabling consequences of TBI, with multiple influences: impairment of neuronal plasticity, metabolomic alterations, loss of vascular homeostasis, and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. The authors take a close look.

Impulsivity has long been thought to be an important risk factor for depression and suicide. But recent research suggests that the reality might actually be counterintuitive.

The topics selected for this special issue highlight the broad relevance of this symptom domain to clinical practice in psychiatry and beyond.

The authors explore ways to address aggression in clinical practice and examine the potentially dangerous impulsivity-violence link across a broad range of conditions.

Suicide and self-harm are often linked to impulsivity, but what do empirical evaluations of this link actually show? This association is discussed and challenged in this article.

The challenges of recognizing behaviors such as hypersexuality, gambling, and excessive buying in Parkinson disease are discussed, as are ways to address them while still managing the underlying condition.