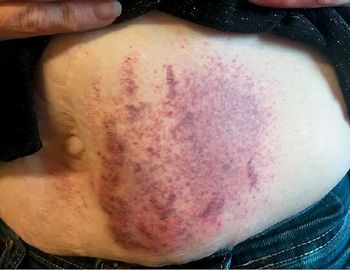
Psychogenic purpura is a rare and poorly understood syndrome. However, early recognition and intervention can lead to remissions which may last years.


Psychogenic purpura is a rare and poorly understood syndrome. However, early recognition and intervention can lead to remissions which may last years.

In the emergency department, how should patients with behavioral disturbances and especially those with illnesses such as dementia, TBI, autism spectrum disorder, and intellectual disability be managed? Take the quiz and learn more.

Psychiatrists may be able to contribute to the care of patients with DM by understanding this problem and its proper treatment. Here's a quiz to test your knowledge.

This article reviews current literature on insomnia and alcohol use disorders and highlights assessment and treatment of sleep disorders in patients with comorbid alcohol abuse.

Clinicians need to consider and manage multiple medical and cognitive comorbidities when working with the elderly population. This slideshow provides an overview of key points relevant to geriatric bipolar disorder as it relates to comorbidity.

Helping patients who have significant medical illness as well as mental illness is a challenge, especially when the diagnosis is unclear. Hospital psychiatrists play a critical role in the management of these behaviorally compromised patients.

Beyond psychosocial implications of anxiety disorders, an array of physiological effects may ensue.

The clinical presentation and functional impacts of ADHD in adults vary greatly from their child and adolescent counterparts.

Psychiatrists can serve a pivotal role in reducing sexual offender recidivism by treating individuals with paraphilic disorders. Details here.

A review of the distinction between depressive and psychotic symptom domains, current knowledge about the etiology and neurobiology of depression and psychosis, and how this knowledge can inform the treatment of patients with features of both.
The authors focus on the psychiatric management of transplant recipients and the evaluation and care of living organ donors.
Psychiatrists are playing an ever-increasing role in the evaluation and care of organ transplant candidates and living organ donors-before and after transplant.

What are the facts regarding co-occurring depression and ADHD?

Potential risk factors related to comorbid ADHD and depression, strategies for proper diagnosis, and treatment approaches.

Insights from the first study of mortality and cumulative psychotropic exposure in schizophrenia.
What is the clinical response to the occasional presence of psychotic symptoms among patients with eating disorders?

The involvement of a psychiatrist early in the care of patients addicted to opioids may prevent further abuse. Here's why.
Because over half of persons with HIV infection have a lifetime history of depression or bipolar disorder, psychiatrists are uniquely positioned to provide both preventive and therapeutic interventions to vulnerable patients.

Personality disorders are arguably the most challenging for psychiatrists because they are difficult to diagnose and frequently coexist with psychotic, affective, and anxiety disorders.

Anxiety is a fundamental aspect of the human experience, but if it impacts social, psychological, or physiological functioning, it can lead to symptoms that cause distress and impairment. Here: the latest on anxiety disorders by experts in the field.

Patients with psychiatric disorders, particularly schizophrenia, anorexia nervosa, and substance use disorders, have reduced life expectancies compared with the general population. This and other facts emphasize the need for the latest clinical information, highlighted in this countdown.

Chronic health problems like diabetes only get worse with depression. New research shows the time is now to address both concerns.

This Special Report focuses on the psychiatric and medical interface of some common medical problems.

Depression and diabetes can prey on the shortcomings of our health care system, such as fragmented, episodic care and poor continuity. Coordinating care can be fraught with difficulties, but it is the goal of many current efforts in health care reform.

The prevalence of chronic hepatitis C virus infection is among the highest in patients with severe underlying mental illness. Here: clinical information on the interface of HCV infection and psychiatric disorders.