
With DSM-5, one more examination of bipolar diagnosis is warranted. After all, if a diagnosis is inaccurate, treatment efforts, however well-intentioned, may misfire.

With DSM-5, one more examination of bipolar diagnosis is warranted. After all, if a diagnosis is inaccurate, treatment efforts, however well-intentioned, may misfire.

Borderline Personality Disorder - Psychogenic Movement Disorders - Myalgic Encephalomyelitis - Migraine

According to the CDC's latest published report, there were 38,364 suicides in the US in 2010-an average of 105 each day. Globally, an estimated 1 million suicides occur annually.

These articles illustrate the variety and complexity of problems associated with comorbidity in psychiatric disorder.

Borderline personality disorder typically coexists with depression, anxiety, and substance abuse. Symptoms of these conditions may lead the clinician to miss the diagnosis of personality disorder entirely. Careful diagnosis of BPD and comorbid disorders is the first step.

Identification of atypical features is important in the treatment of depression for both treatment selection and prognosis, especially when initial measures prove ineffective. The concept of atypical depression has evolved over many years, and now it appears timely for a further revision.

A plethora of studies support the hypothesis that inflammation plays a role in the pathophysiology of major psychiatric disorders.

Given the likelihood that insufficient numbers of patients will be available for a randomized controlled trial of MAOIs in refractory depression or atypical depression, we must still rely on consensus guidelines and expert opinion.

DSM-5 presents psychiatry with a potential “reset button” for diagnostic reliability.

Four studies sprang from the TORDIA trial on treatment-resistant depression in children and adolescents and showed that several factors influence treatment efficacy following treatment resistance.

The role of subtyping and bipolarity in TRD was discussed in Part 1 of this 2-part article. Here we review a number of the most common confounding factors of TRD but limit our scope to comorbidities that can be directly addressed and treated by psychiatrists.

The current system of payment for mental health care in the US can lead, or even incentivize, clinicians to focus on and code for Axis I disorders and their more readily reimbursed psychopharmacological treatment approaches.

Melatonin has a role in psychiatric illness and the treatment of circadian rhythm sleep disorders, insomnia, and comorbid depressive disorders.

Research is needed to define clinical biomarkers and genetic screens that could be used to identify early stages of dementia and to link clinical syndromes with the later development of dementia.

The New York Times ran a front-page story regarding numerous controversies surrounding the DSM-5, most notably, the issue of eliminating the so-called bereavement exclusion in diagnosing a major depressive episode. Here, Dr Pies responds to Dr John Grohol, Psychologist and Editor of the Psychcentral Web site.

The designer of the DSM-5 Field Trials has just written a telling commentary in the American Journal of Psychiatry. She makes what I consider to be 2 basic errors that reveal the fundamental worthlessness of these Field Trials and their inability to provide any information that will be useful for DSM-5 decision making.

This essay is a brief update on an earlier Psychiatric Times article by Dr James Phelps. Several major studies have appeared since the publication of the original article, which shed further light on this issue.

Understanding pediatric psychopharmacology in the context of medical illness.

When I was a first-year resident, a revered supervisor of mine made the statement-half-facetiously-that, “In psychiatry, you can do biology in the morning and theology in the afternoon!”

Several available agents in addition to methylene blue are being investigated for bipolar disorder and were in a in a recent review.

A dark cloud surrounds the silver lining of having one psychiatrist in a position of almost unopposed influence . . .

Dear Mrs. -- You have asked me about the cause of your mood disorder, and whether it is due to a "chemical imbalance."

The DSM-5 Scientific Review Group was the last hope for an eleventh hour DSM-5 save. This hope recently died.
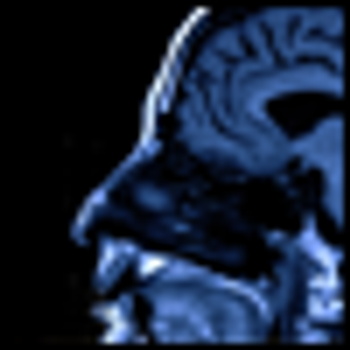
This article addresses the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of mild TBI among combat veterans, with a particular focus on blast injury and the presence of comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).

The majority of the literature focuses on prenatal and postnatal depression in mothers, and little attention has been given to the incidence of prenatal and postpartum depression in fathers.